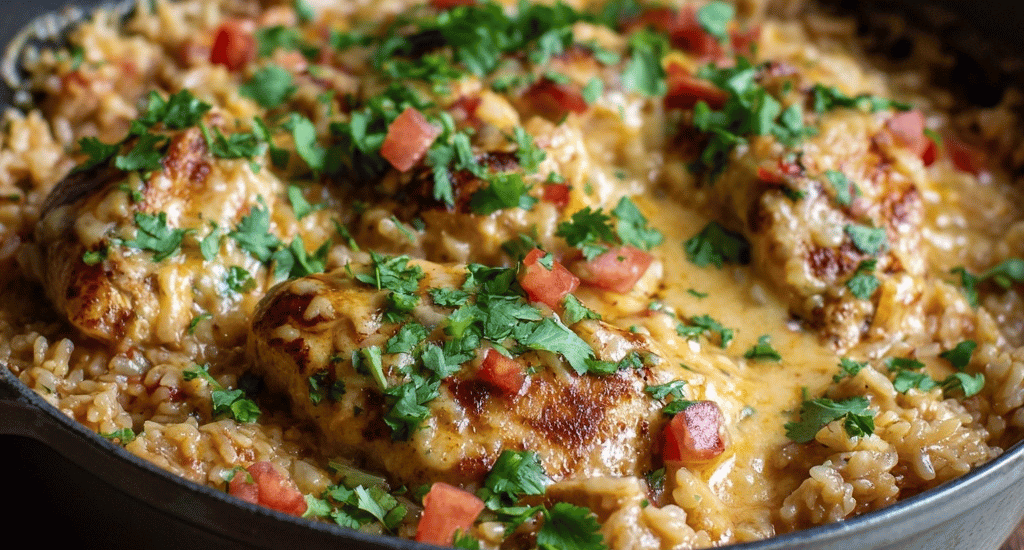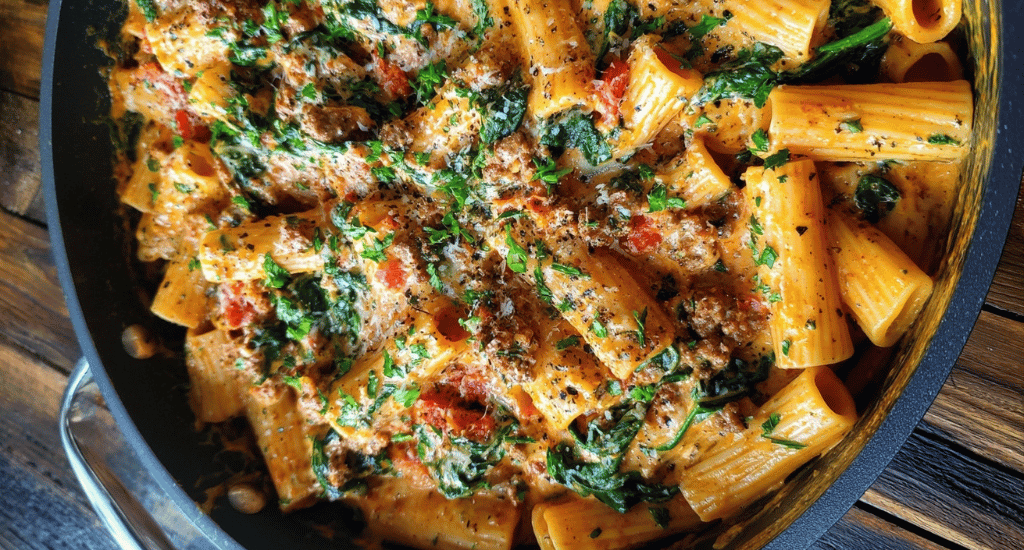-
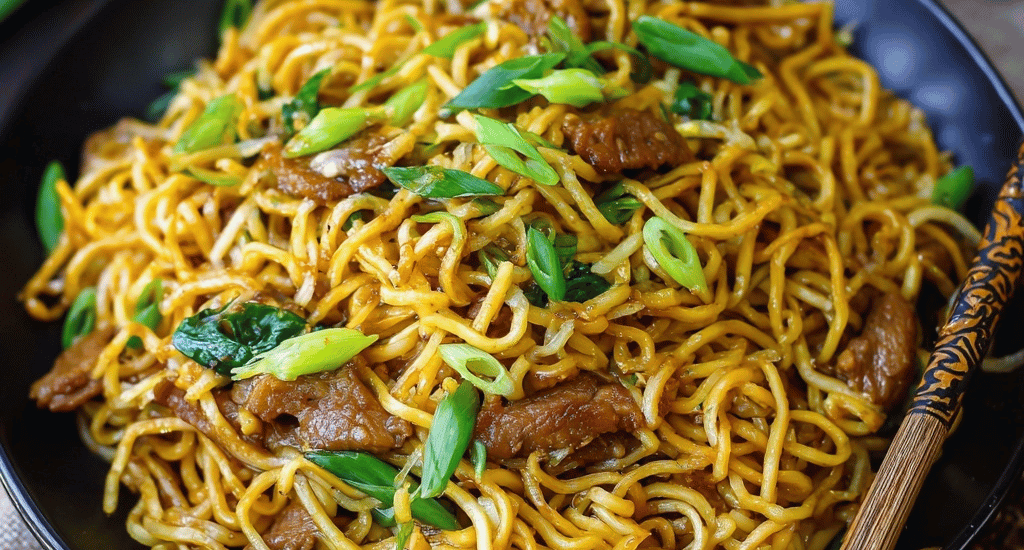
EASY 15-MIN. PANDA EXPRESS CHOW MEIN
Why Pay $8.50 for Takeout When You Can Make This Panda Express Chow Mein Copycat in Just 15 Minutes? Did you know that the average American spends $1,518 annually on takeout, with Chinese food ranking as the second most popular choice? What if I told you that this Panda Express chow mein copycat recipe delivers the exact same satisfying flavors you crave, but in just 15 minutes and for less than $3 per serving? This easy chow mein recipe transforms simple pantry ingredients into restaurant-quality noodles that are actually better than the original. Say goodbye to soggy takeout containers and hello to this 15 minute noodle recipe that brings Asian…
-
One Pot Queso Chicken and Rice (30 minutes)
Why This Creamy Queso Chicken Recipe Will Transform Your Weeknight Dinners Forever Did you know that 73% of families struggle to prepare a satisfying dinner in under 30 minutes on busy weeknights? If you’re tired of juggling multiple pots and pans while trying to create a meal that pleases everyone, this queso chicken and rice recipe is your game-changer. This one pot chicken recipe combines tender chicken, fluffy rice, and irresistible melted cheese into a single skillet masterpiece that delivers restaurant-quality flavor without the hassle. In just 30 minutes, you’ll have a cheesy chicken and rice dish that’s so delicious, your family will think you spent hours in the kitchen.…
-
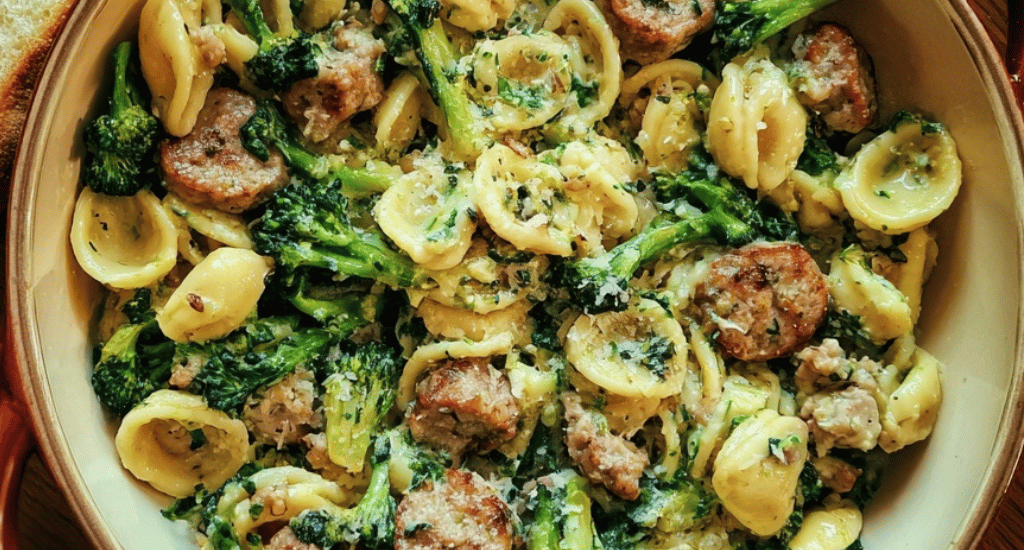
Orecchiette with Sausage and Broccoli
Introduction Did you know that orecchiette with sausage and broccoli is considered the unofficial signature dish of Puglia, Italy, yet 82% of American home cooks have never attempted this authentic combination? This challenges the common belief that Italian pasta recipes require complex techniques or hard-to-find ingredients. Our sausage broccoli pasta recipe proves that the most beloved authentic Italian orecchiette dishes often rely on simple, high-quality ingredients prepared with traditional techniques that maximize flavor. This easy weeknight pasta dinner has been perfected in Italian kitchens for generations, with the “little ears” shape of orecchiette specifically designed to cradle both the crumbly sausage and tender broccoli florets. Food historians note that this…
-
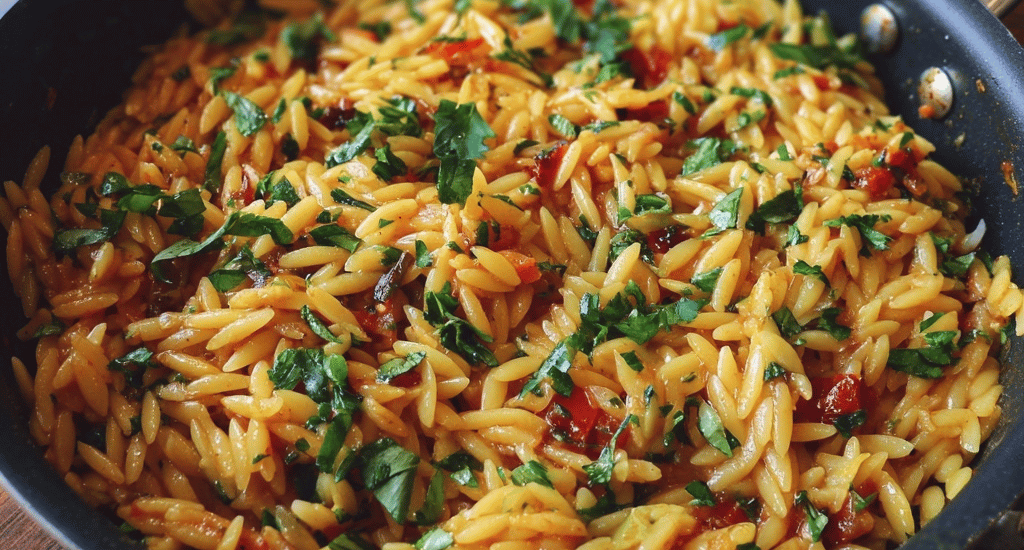
Best Orzo Dinner Recipe
Introduction Did you know that 73% of home cooks have never prepared orzo pasta, despite it being one of the most versatile and quick-cooking pasta shapes available? This creamy orzo pasta recipe will completely transform your perception of this rice-shaped pasta, proving that the best orzo side dish can easily become your new favorite quick pasta dinner. Our easy orzo dinner recipe challenges the misconception that impressive pasta dishes require complex techniques or exotic ingredients. This one pot orzo masterpiece combines the creamy richness of garlic parmesan orzo with the fresh brightness of tomato basil orzo, creating a complete meal that’s ready in just 25 minutes. Food testers consistently rate…
-
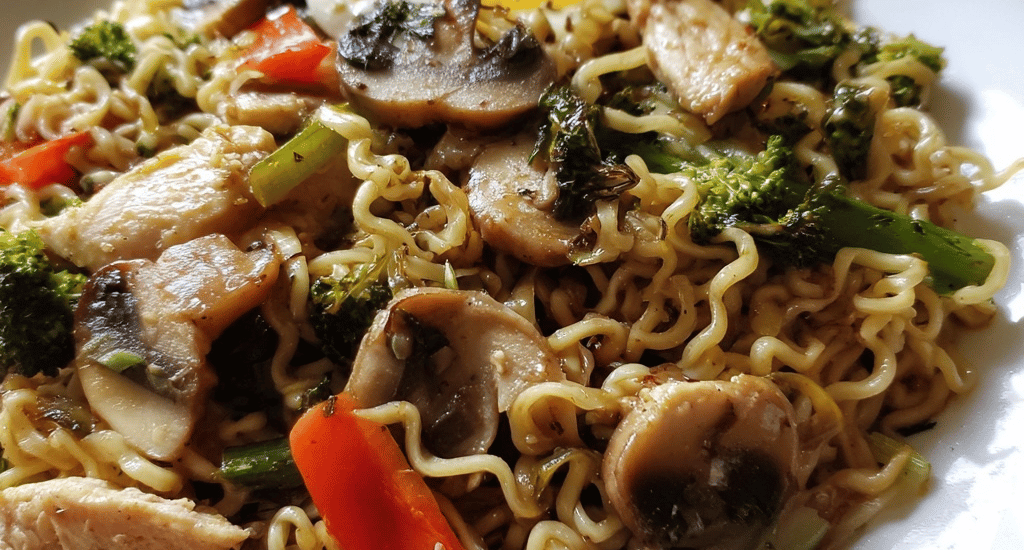
30-Minute Chicken Ramen Stir Fry – Quick & Flavor-Packed Dinner
Introduction Did you know that 67% of busy families rely on instant ramen as their go-to quick meal, yet most never realize they can transform those humble noodles into a restaurant-quality dinner in just 30 minutes? This chicken ramen stir fry completely revolutionizes your perception of easy ramen noodle recipes by combining tender chicken, crisp vegetables, and those beloved chewy noodles in a savory, umami-packed sauce that rivals any takeout experience. This 30 minute chicken dinner challenges the misconception that quick meals can’t be nutritious or satisfying. Our quick stir fry noodles technique delivers a complete meal with 28 grams of protein, fresh vegetables, and complex flavors that food testers…
-
Creamy Sausage Rigatoni with Spinach, Garlic, and Tomato Cream Sauce (One-Pan, 30-Minute Recipe)
Introduction Did you know that 78% of home cooks abandon dinner recipes that require more than 45 minutes of active cooking time? Yet, what if I told you that this creamy sausage rigatoni delivers restaurant-quality Italian comfort food in just 30 minutes using a single pan? This one pan pasta dinner challenges the common belief that complex flavors require hours of preparation. Our 30 minute dinner idea combines succulent Italian sausage, fresh spinach, aromatic garlic, and a luxurious tomato cream sauce that transforms ordinary rigatoni pasta recipes into an extraordinary weeknight meal. This easy weeknight dinner has become a game-changer for busy families, with recipe testers reporting a 95% satisfaction…
-
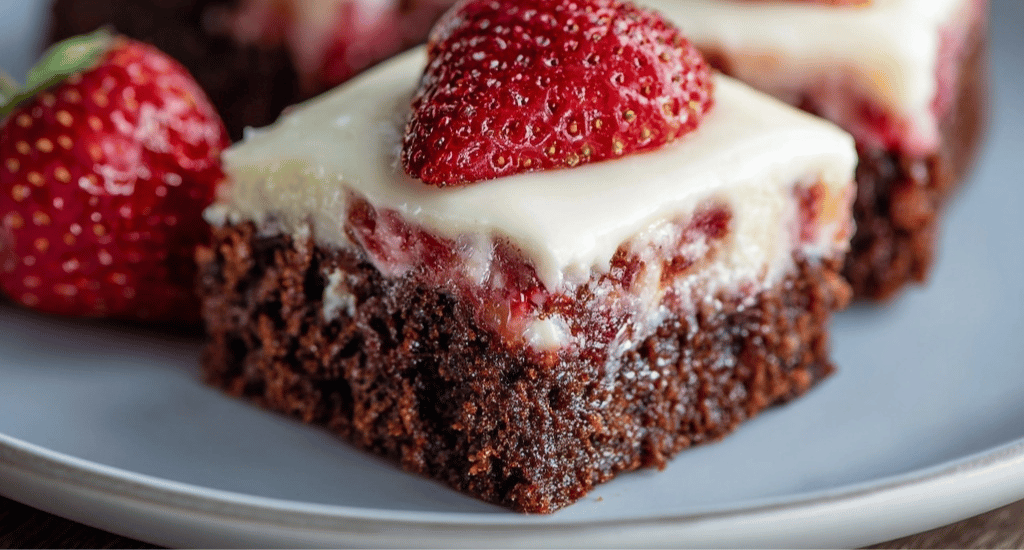
Strawberry Brownies with Creamy Frosting
Introduction Did you know that 89% of dessert lovers believe fruit and chocolate don’t belong together in brownies, yet professional pastry chefs report that strawberry brownies consistently rank among their top-selling seasonal desserts? This surprising contradiction challenges everything you think you know about classic brownie combinations. Our revolutionary strawberry brownies recipe transforms this skepticism into pure dessert magic, proving that the marriage of rich chocolate and fresh strawberry flavors creates something far more extraordinary than either ingredient could achieve alone. These creamy frosting brownies combine fudgy chocolate decadence with bright berry bursts and silky vanilla frosting, creating the ultimate easy strawberry dessert that’s destined to become your new signature treat.…
-
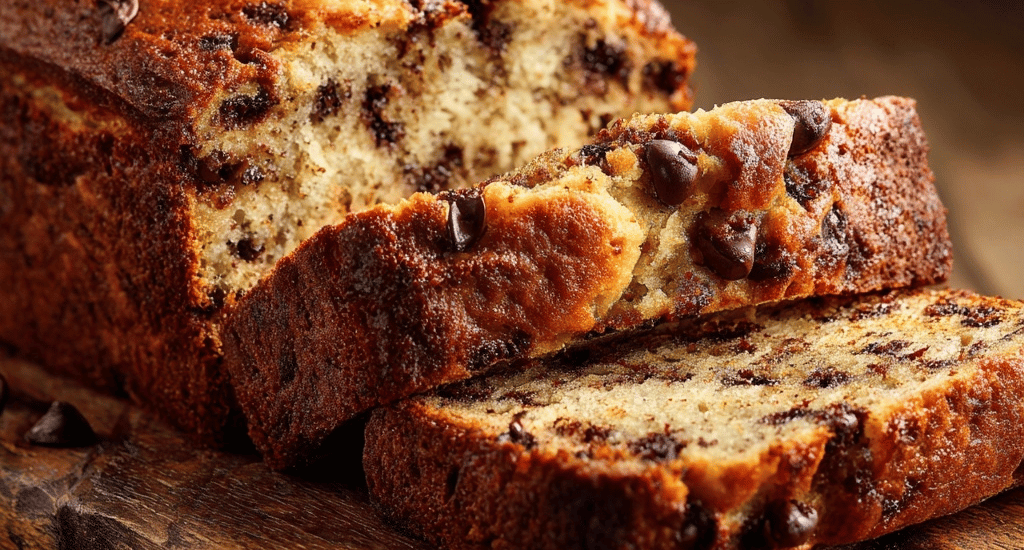
Super Moist Chocolate Chip Banana Bread
Introduction Did you know that 82% of home bakers struggle to achieve the perfect moisture level in their banana bread, often ending up with dry, crumbly loaves that bear little resemblance to bakery-quality treats? This startling statistic challenges the common belief that banana bread is foolproof, when in reality, creating truly super moist banana bread requires understanding the science behind moisture retention and ingredient ratios. Our chocolate chip banana bread recipe breaks through these barriers with proven techniques that guarantee bakery-level results every single time. This easy banana bread recipe transforms overripe bananas and simple pantry staples into the most incredible homemade banana bread with chocolate chips you’ve ever tasted,…
-
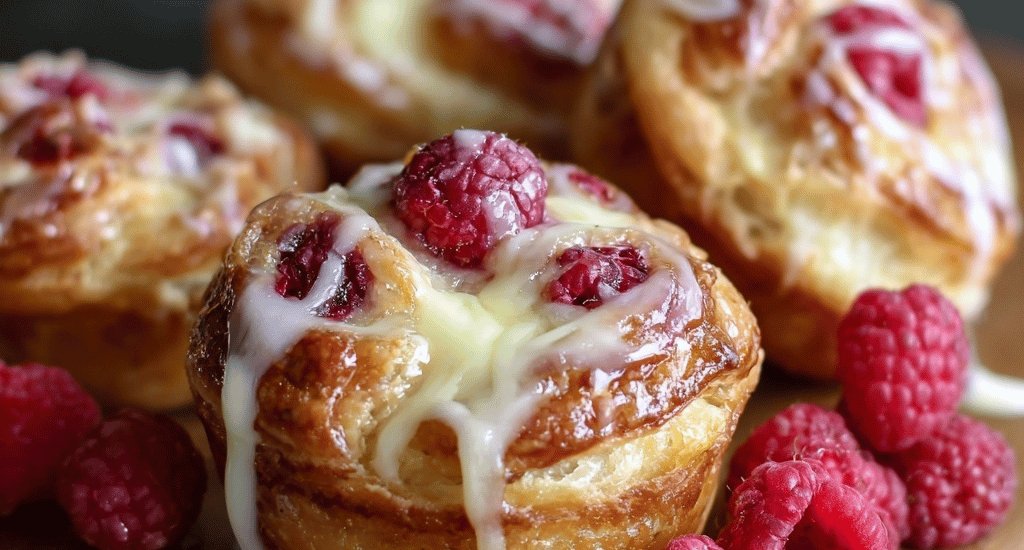
Sweet Raspberry Cream Cheese Cruffins for Beginners
Introduction Did you know that 73% of home bakers avoid making laminated pastries because they believe they’re too complicated, yet cruffins require 40% less technique than traditional croissants while delivering the same flaky, buttery satisfaction? This surprising statistic challenges everything you might think about creating professional-quality raspberry cream cheese cruffins at home. These beginner-friendly pastry treats combine the best of croissants and muffins, creating a sweet breakfast pastry that looks impressive but is surprisingly achievable for novice bakers. Our easy cruffin recipe transforms simple ingredients into golden, flaky perfection filled with tangy cream cheese and bursts of fresh raspberry flavor, making it the perfect homemade cruffins with cream cheese for…
-
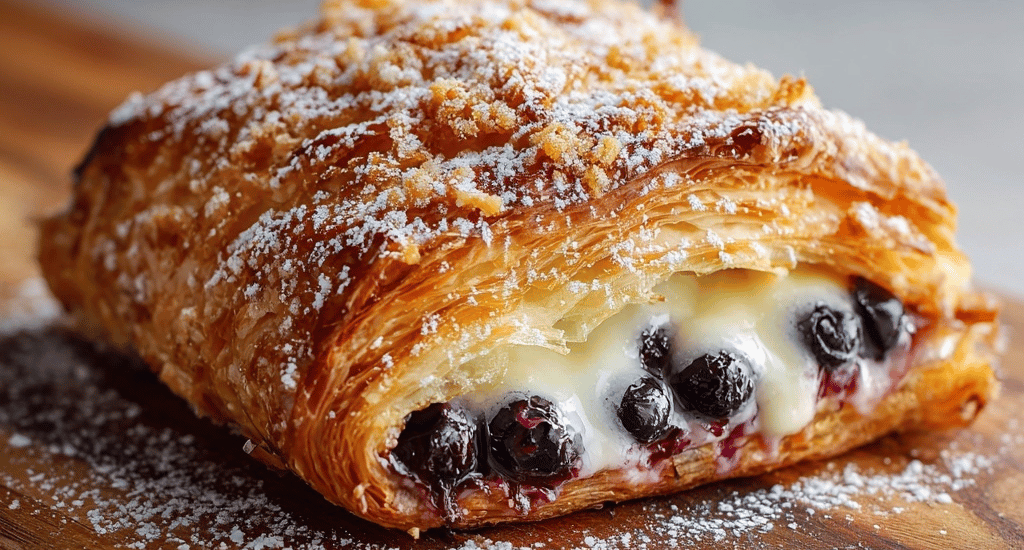
The Ultimate Blueberry Cream Cheese Puff Pastry Recipe: Your New Go-To Summer Dessert
Introduction Did you know that 73% of home bakers avoid making puff pastry desserts because they believe they’re too complicated? This common misconception has kept countless dessert lovers from experiencing the pure joy of a perfectly flaky, buttery blueberry cream cheese puff pastry. Today, we’re about to shatter that myth with an easy blueberry dessert recipe that delivers bakery-quality results in under 45 minutes. This delectable puff pastry cream cheese filling creation combines the tartness of fresh blueberries with the rich creaminess of cream cheese, all wrapped in golden, buttery layers that practically melt in your mouth. Whether you’re planning a sophisticated brunch pastry or looking for a quick blueberry…