“What Could Red Dots on Your Skin Signify?”
Causes of Red Spots on the Body
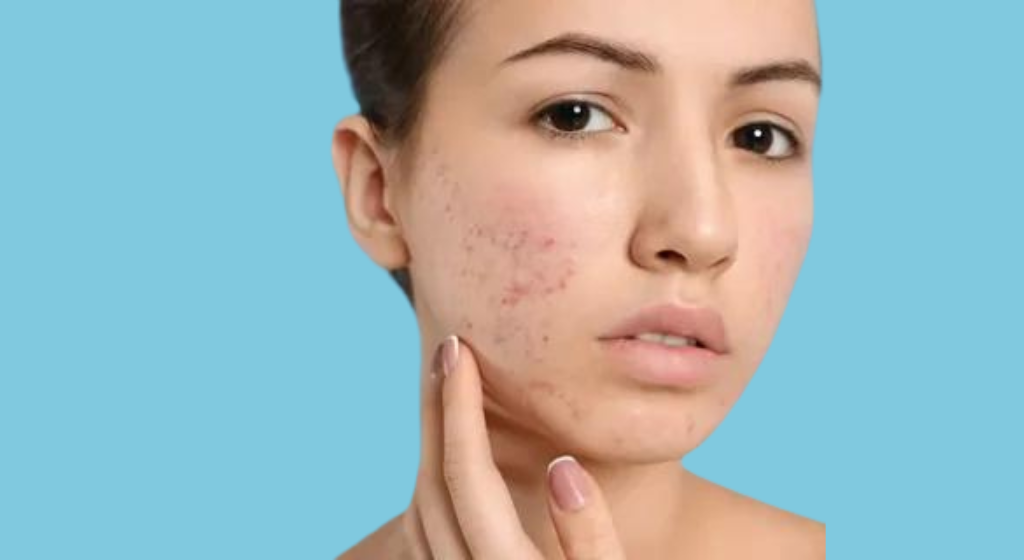
Red spots on the body can be common. Although these spots are often harmless, they can sometimes indicate an underlying health condition. They can appear suddenly or gradually over time, depending on the cause.
These red spots vary in size, location, and appearance. They may be flat or raised, painful, or itchy, and their colors range from light pink to dark red.
Types of Red Spots on the Body
Red spots on the body can appear in several forms, including:
- Rash: A widespread irritation or inflammation of the skin caused by infection, allergens, or irritants.
- Skin lesions: These can appear as red bumps or a flat rash.
- Erythema: A medical term that refers to reddening of the skin due to a specific cause.
- Pustules: Raised red spots filled with pus.
- Bleeding spots: Small red or purple spots caused by bleeding under the skin.
- Hemangiomas: Small, benign red growths made up of blood vessels.
- Purple spots: Larger red-purple spots caused by blood pooling under the skin.
Conditions associated with red spots and their treatment
- Psoriasis rosacea:
This inflammatory skin condition typically begins with a large, oval red spot on the chest, back, or abdomen. Soon after, smaller red spots appear on the rest of the body, resembling ringworm of the scalp. The cause is unknown but is thought to be viral. While the spots may be itchy and accompanied by a fever, sore throat, or headache, the condition often goes away on its own. Anti-itch lotions, such as calamine, can provide relief. - Contact dermatitis:
This itchy rash occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, causing redness, swelling, and sometimes blisters. Treatment involves avoiding the trigger and using antihistamines or topical creams to relieve symptoms. Severe cases may require medical treatment. - Heat rash:
This condition is caused by skin irritation from excessive heat or moisture, and often affects the folds of the skin. The rash appears as small red spots or itchy blisters, and may sting or tingle. Staying in a cool, dry place can help, and severe cases may need medical intervention. - Shingles:
Shingles is a viral infection that causes a painful red rash or blisters, usually on one side of the body. It is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. It usually starts with a burning sensation before developing into blisters. Treatment usually involves antiviral medications and pain relievers. - Swimmer’s itch:
This itchy rash is caused by parasites in contaminated water. Symptoms include small red blisters and a burning sensation. The condition usually goes away on its own within a week, but anti-itch creams can help manage the discomfort. - Tinea of the scalp:
Tinea of the scalp is a fungal infection that causes a red, circular rash with raised edges. It is highly contagious and requires prescription antifungal treatments. - Atopic dermatitis (eczema):
This is a chronic skin condition that causes red, cracked, dry patches. It is common in children and may persist or recur in adulthood. Moisturizing and medicated creams can help manage symptoms. - Psoriasis:
Psoriasis causes an overproduction of skin cells, resulting in thick, scaly red patches, often with silvery scales. It can appear anywhere on the body and requires medical treatment to control flare-ups. - Drug rash:
Certain medications can cause allergic skin reactions, resulting in different types of rashes, including red bumps or peeling skin. The rash usually goes away once you stop taking the medication. - Insect Bites:
Bites from mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, and other insects can cause itchy, red bumps. Over-the-counter medications usually provide relief, although severe reactions may require medical attention.
Other Possible Causes
Red spots can also be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, as well as bleeding disorders. Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Serious Conditions Associated with Red Spots
In some cases, red spots can indicate a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. These include:
- Leukemia
- Meningitis
- Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis)
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)